Frequently Asked Questions
About Kidney Diets
‘Advice from the Kidney (Renal) Dietitians on the importance of adequate energy in your kidney diet.’
Sufficient energy intake is important as part of your kidney diet, to help maintain your weight and muscle stores and ensure you have enough energy to perform the basic activities of daily living such as washing and dressing.
Our bodies get energy from the foods we eat and drink. Foods containing carbohydrates, protein and fat are used by our bodies to provide energy. The amount of energy (calories) we need depends on our age, size, gender, physical activity level and nutritional status (e.g. overweight or underweight). Starchy foods e.g. potatoes, rice, pasta, bread and breakfast cereals are good sources of energy and provide valuable energy (calories) in the kidney diet. A starchy food should be included at each meal to ensure an adequate energy (calorie) intake. Speak to your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian to receive an individualised kidney diet meal-plan.
The Challenges
When you or your family member have kidney disease meeting energy (calorie) needs may be challenging. Many people with kidney disease experience a reduced appetite and taste changes, which are associated with elevated urea levels (waste product level). These symptoms commonly result in a poor dietary intake and unnecessary weight loss if not addressed. Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will be able to provide you with individualised advice to manage your appetite and weight.
Conversely if you are overweight or obese a recommendation for weight reduction may be made, to aid the management of your kidney disease or to facilitate your eligibility for a transplant.
If you are trying to reduce your weight a reduction in your energy intake may be required to facilitate this, your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will provide you with a tailored weight reduction plan.
‘Dietary protein in adequate amounts is required for normal body function, growth and repair but too much is not recommended in Chronic Kidney Disease. Here the Kidney (Renal) Dietitians explain about protein needs & the kidney diet’
Dietary protein is important for normal function, growth and repair in all parts of the body, including the skin, muscles, blood and internal organs. Meat, fish, chicken, eggs and milk are foods rich in protein. Other foods, such as bread, pasta, rice and potatoes also contain protein in smaller amounts.
How much protein do I need to eat in my Kidney (Renal) diet?
The amount of protein you need depends on your stage of kidney disease, your size and whether or not you are on dialysis. Most people with kidney disease who are not on dialysis need to eat a moderate amount of protein. Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will give you a daily protein allowance and discuss with you how you can make small changes to your Kidney (Renal) diet to achieve this. Your Dietitian may guide you to estimate a serving or portion of protein as follows:
1oz cooked meat = a small matchbox size
3oz cooked meat = a deck of playing cards or average sized adult palm
Add in descriptor from RIG diet sheet – 1 cooked chicken breast =
Dietary Protein and Dialysis
When people start dialysis, they are usually advised to increase the protein they eat in their kidney diet. This is because a small amount of protein is lost with each dialysis session.
What happens if I get too much or too little protein in my kidney diet?
Eating too little protein can cause: Eating too much protein can cause:
* Muscle Weakness * Nausea and Vomiting
* Fluid Retention / Swelling at the ankles * High levels of urea
* Poor health * Loss of Appetite
* Losing muscle instead of fat * Fatigue
You may need more protein if you have an infection, or a wound to heal. If you cannot meet your protein needs with food alone, you may require a protein supplement. It is important to discuss this option with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian before commencing any supplements.
Blood tests and Protein
Albumin is a type of protein found in the blood. It can be used to evaluate your nutritional status. A low albumin on your blood test can mean that you are not getting enough protein in your kidney diet. You should discuss this with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Phosphate Binders and Dietary Protein
If you have been prescribed a medicine called a phosphate binder, remember to take your binders as prescribed, as all foods that are high in protein are also high in phosphate.
‘Learn to adapt your favourite home cooked foods making them suitable for your kidney diet’.
The good news is that, many standard cookbooks or celebrity chef recipes can be used safely through a little adaptation and some imagination to make them lower in potassium, sodium and phosphate.
To help you to identify any adaptation required, we recommend that you read each new recipe (or old favourites) with your kidney (renal) diet allowances clear in your head and your diet sheet of foods best avoided close to hand. Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian can help you to adapt recipes or review those that you have self adapted.
Here are some suggestions to make your favourite recipes more kidney friendly:
Tips to help you to become a kidney friendly baker:
- Use reduced amounts of salt or omit it all together from the recipe. Use herbs and spices (e.g. nutmeg, cinnamon) instead of salt to add flavour.
- Reduce the phosphate content of a recipe by using white flour or half white and half whole wheat flour instead of all whole wheat flour.
- Use yeast, bread soda / bicarbonate of soda as a raising agent instead of baking powder. Breads and cakes will then be lower in phosphate than those using baking powder. Bread soda / bicarbonate of soda require an acidic fluid like lemon juice or buttermilk to act as a raising agent. Be sure to include these in your daily allowances.
- Choose lower potassium fruits when baking tarts, muffins and fruit pies such as apple, pear, pineapple, cranberries and blueberries or drained tinned fruit (remember to include the fruit as part of your daily kidney diet fruit allowance).
- Choosing the unsalted varieties of butter for baking will make a recipe more kidney friendly by reducing the salt (sodium) content.
- Double cream plus water is a good alternative to single cream or milk. Making this simple change will lower the phosphate content of the recipe and help you with your daily dairy allowances (reduced phosphate kidney diet).
- Unfortified rice milk is lower in potassium and phosphate than cow’s milk and may be used to make puddings.
- Use egg whites as they are lower in phosphate than egg yolks and are useful for desserts e.g. meringues.
Making main meal dishes kidney friendly:
- Reduce potato intake to reduce dietary potassium intake. Use rice, pasta, noodles, couscous or breads instead of potatoes with main meals. This will lower the overall potassium content of the dish.
- Avoid prepared tomato sauces. Try a small amount of fresh tomato instead, or if making a pasta dish, use olive oil and garlic instead of a tomato based sauce to dress / flavour the pasta. This will lower the potassium content and make your pasta dish more Kidney friendly.
- To lower potassium content, vegetables can be par boiled before being added to recipes (e.g. carrots, broccoli or cauliflower in a curry). If you are following a strict low potassium kidney diet, fully boil your vegetables (link low potassium vegetable cooking instructions page) and add to the composite meal (e.g. kidney friendly stew, curry) for the last 10 – 15 minutes of cooking.
- For dishes that contain high potassium vegetables e.g. Mushrooms, substitute them for lower potassium vegetables e.g. Green (French) beans
- For stir-fry dishes avoid using higher potassium vegetables such as pak choi, bamboo shoots or mushrooms. Substitute them with Green (French) beans, Bean-sprouts or Cabbage. If you require a strict low potassium kidney diet, remember that stir fry vegetables retain a high percentage of potassium during cooking. Link with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian and discuss your kidney diet allowances.
- To reduce salt (sodium) intake in your kidney diet, avoid using regular soy sauce, limit reduced salt (sodium) soy sauce to small amounts and limit the amount of other high salt (sodium) sauces such as fish, oyster, teriyaki or sweet and sour sauces. Try using vinegar, ginger or a little sesame oil as alternative flavourings to make a meal more kidney friendly.
- Double cream plus water is a good alternative to single cream or milk in savoury dishes. Making this simple change will lower the phosphate content of the recipe and help the recipe to fit into the daily allowances of a reduced phosphate kidney diet.
- If dishes contain cheese, use this sparingly or choosing a lower
phosphate cheese e.g. Brie, camembert, parmesan, feta, cottage or cream cheese. - Make a fish dish more Kidney friendly by substituting shellfish or smoked fish in the recipe for white fish such as cod, whiting or plaice. This will reduce the salt (sodium)and phosphate content of the dish.
- To reduce salt (sodium) content use low salt stock cubes (link to low salt stock cube page) as recommended by your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian as a base for stock. Do not add any extra salt.
‘Managing fluid intake is often a balancing act when you have kidney disease. Here, the Kidney (Renal) Dietitians give tips to help you with this tricky part of the Kidney (Renal) Diet’
When your kidneys are not working properly, you may not be able to get rid of enough fluid from your body. A build up of fluid can lead to problems such as high blood pressure, swelling of the ankles & shortness of breath. How much fluid you should have each day depends amongst other things on how much kidney function you have left, if you are on dialysis or not, and how much urine you pass.
If you require any changes to your fluid intake (a fluid allowance) as part of your kidney diet, Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will have this information and will develop an individualised fluid and kidney diet plan for you.
Tips to help you manage your fluid intake and your kidney diet:
Reduce thirst by reducing salt
- Avoid adding salt to foods. Salt holds onto fluid in the body and increases thirst. (link to salt information).
- Use Fresh foods in preference to processed foods to reduce salt intake. About 65 – 70% of the salt we eat comes from processed foods, fast food, canteen and restaurant food (Irish Heart Foundation 2012). Salt increases thirst.
Reduce Volume of fluid
- Use a small cup/glass and divide out your fluid intake over the day. Keeping a written record of your intake is helpful to keep track of your kidney diet fluid allowance.
Typical household measures to help you add up your fluid intake each day:
A mug = 300mls
A Standard Water Glass = 200mls
A Small cup = 150mls
A Tablespoon = 15mls
A small ice cube = 15ml
- Foods with high water content include: soup, ice cream, jelly, custard, rice pudding, sauces, and gravy. Cut down or even avoid some of these foods if fluid retention (gain) is a problem.
Avoid a Dry Mouth – keep it Fresh!
- Keep your mouth feeling fresh by chewing gum, brushing your teeth or rinsing with mouth wash regularly. Discuss your dry mouth with your Kidney (renal) Dietitian as artificial saliva sprays and gels may be suitable for you.
- Sucking on an ice cube can help relieve thirst whilst using the smallest amount of fluid. Try freezing some diluted squash in your ice cube tray to add some flavour. If you have Diabetes, use a ‘No Added Sugar’ variety.
AVOID |
TRY INSTEAD |
|---|---|
| Meat
Liver, kidney, pate, sausages, salami, meat pastes |
Fresh Beef, Lamb, pork, chicken, turkey |
| Fish
Crab, sardines, kippers, whitebait, fish roe, monk fish, sea bass, prawns, bones of tinned fish |
Fresh Cod, Whiting, plaice, lemon sole, tuna, salmon |
| Bread, rolls and scones
Naan bread, soda bread, scones |
Ciabatta, garlic bread, pitta, white sliced bread, brown sliced bread, baguettes, croissants, granary rolls, soft & crusty white rolls. |
| Rice and Pasta
Brown Rice and brown pasta |
White Pasta, plain noodles, basmati rice, white rice |
| Breakfast Cereals
All Bran, Branflakes, muesli, cereals containing nuts or chocolate, Ready Brek, wheat germ. |
Porridge, Weetabix, Oatibix, Shredded Wheat, Cheerios, Rice Krispies, Special K, Cornflakes, Frosties*, |
| Biscuits, cakes, pastry, buns
Oat based biscuits, oatcakes, flapjacks, rye crispbreads, and biscuits containing nuts or chocolate, scones, cake mixes, waffles, cakes containing nuts or chocolate, instant dessert mixes. |
In moderation*, Gingernuts, custard creams, jammy dodgers, Jam rings, Shortcake, Shortbread, Madeira cake, pastry, doughnuts, jam tarts, crumbles, tarts, lemon meringue pie More suitable in moderation on a reduced sugar diet Rich Tea, Marietta, Lincoln, Digestives, water biscuits, cream crackers Please note: that a considerable number of the above suggestions are a source of added phosphates and should be considered as “treat foods”. |
| Sweets / snack food
Chocolate and foods containing chocolate such as cakes, bars or sweets, fudge, toffees, cereal bars, nuts |
In moderation*, Boiled Sweets, marshmallows, jellies, mints, Turkish delight (no chocolate)
|
| Beverages
Horlicks, Ovaltine, Drinking Chocolate, Complan, Build Up, Cola Drinks
|
Tea, lemonade, tonic water, lucozade, ginger ale. You can use most dilutible drinks – check the label and avoid those with a fruit juice content of more than 12% |
‘A high potassium level in your blood stream is serious and can cause an irregular heart beat leading to a crisis medical situation and in some cases a heart attack. Learn more about potassium here and how your kidney diet plays a key role in protecting your heart and maintaining your safety’
What is Potassium?
Potassium is a mineral. It is found in many foods in different amounts. Some foods are known to be higher in potassium than others, for example: potatoes, fruit, vegetables, dairy foods (milk based foods) and protein foods (meat, poultry, fish and eggs).
You will hear these foods referred to as High Potassium Foods.
What is the function of Potassium?
Potassium’s main function is in muscle contraction. It helps control the contraction of the heart.
What should my levels be?
It is important that you understand what a normal level is and also know your own potassium level. On average a normal potassium level in our blood is between 3.5-5 mmol/L. Anything above 5mmol/l indicates a high potassium level (please note laboratory reference ranges may differ from hospital to hospital. Ask you Kidney (Renal) Dietitian what reference ranges are used in your hospital).
What causes a high Potassium level?
When you eat a food high in potassium, the level of potassium in your blood will increase. One of the functions of the kidney is to clear this excess potassium from your blood and keep your levels safe.
If your kidney is not functioning properly the level of potassium could remain dangerously high.
Consequences of high potassium?
High levels of potassium can be dangerous.
Some of the signs and consequences of high potassium include: muscle weakness, weak legs and a tingling sensation. If left untreated, the consequences of a high potassium level can result in a heart attack.
‘A high salt intake holds onto water, increases blood pressure and increases thirst making it harder to follow your kidney diet and fluid restriction. The Kidney (Renal) Dietitians explain here why it is better to leave the salt in the sea!’
Salt or sodium chloride is needed in very small amounts in the body for maintaining water balance, healthy blood pressure and healthy muscles and nerves. However, too much salt in your kidney diet may lead to increased thirst, high blood pressure and cause your body to hold onto too much fluid. This extra fluid puts extra pressure on your heart to pump blood around your body, thus the more fluid you retain the higher your blood pressure will be. Increased thirst can make it difficult to maintain your fluid restriction.
Even without adding salt to your food, you can easily get more than you need by including processed foods that have a high salt content in your kidney diet. It can take up to six weeks for your taste buds to adjust to having less salt, but soon you should find that you are enjoying the real flavour of your food.
To reduce your salt intake:
- Avoid using salt at the table and if needed use only a pinch of salt in cooking.
- Choose fresh foods instead of processed and canned foods.
- Use herbs and spices instead of salt in cooking and at the table.
- Check food labels for the salt / sodium content to help make healthier choices.
It is important not to use salt substitutes such as Lo Salt and So-Low, as they are very high in potassium.
Avoid having the following foods as they contain large quantities of salt:
- Bacon, sausages, black and white puddings processed meats (corned beef, salami, pâté)
- Frozen and take away meals, convenience foods, meals containing soy sauce.
- Smoked fish and fish pastes
- Tinned vegetables (unless marked ‘no added salt’)
- Tinned and packet soups, casserole mixes (e.g. Bovril, Oxo, Marmite), stock cubes
- Bottled canned and packet sauces and tomato juice
- Crisps, salted biscuits (e.g. Tuc, Ritz) and other salted snacks e.g. nuts and popcorn
- Keep to less than 100g (4oz) cheese a week. Refer to your individualised dairy allowance as provided by your Renal (kidney) Dietitian.
- Avoid salt substitutes.
‘A high phosphate level in your blood (hyperphosphataemia) can over time, shorten your life, weaken your bones, harden your blood vessels, cause painful soft tissue sores and lead to itchy skin. Here, the Kidney (Renal) Dietitians explain this critical component of the Kidney (Renal) Diet’
Phosphate is a mineral found in foods that is necessary for strong bones. Our kidneys filter it out of our blood if we eat too many high phosphate containing foods. When your kidneys are not working as well as they should be, they are unable to remove excess phosphate from your blood. This leads to an increase in the level of phosphate in your blood (hyperphosphataemia).
High levels of phosphate in the blood may weaken your bones and lead to hard deposits in certain parts of the body, including your eyes, joints, skin, heart and blood vessels. Over time this can lead to restricted blood flow and heart disease. Itchy skin may be a sign that your phosphate levels are too high. However you may not realise that your phosphate level is high as you may not feel any different.
To help control phosphate levels in your body, it is important to eat a low phosphate kidney diet. To do this you will need to; limit the amount of dairy products you eat, keep to your daily limit of high protein foods and avoid other foods that contain a large amount of phosphate.
Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will give you specific advice on how much dairy and high protein foods you should have and also advice on particular foods to avoid (refer to section on the website “phosphate swap shop” for some more information on phosphate containing foods and better options to choose.).
As phosphate is widely used in the food industry you will also need to look out for hidden sources of phosphate in processed foods. To help stick to your low phosphate kidney diet, check the food label for ingredients that contain the word phosphate such as diphosphates, sodium polyphosphate and phosphoric acid.
Don’t eat foods containing these ingredients.
If a low phosphate kidney diet alone does not bring your phosphate to a normal level then you may need to take a tablet called a phosphate binder with your meals and snacks. Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will let you know if you need phosphate binders. There are a number of different binders available.
The amount and type of phosphate binder prescribed for you may change over time depending on your phosphate levels. Phosphate binders must be taken at the correct time as advised by your Doctor or Kidney (Renal) Dietitian to work effectively.
It is important that you monitor your own phosphate levels and take control of your dietary phosphate load.
What do kidneys do and what is kidney disease?
‘Measuring the size of a fist and located in your lower back, the kidneys are a hive of activity. Click here to find out more about what kidneys do and what is kidney disease?’
The kidneys are two bean shaped organs located in your lower back. Each kidney is about the size of a fist and weighs about 4-6oz. Inside the kidneys are tiny structural and functional units call nephrons which filter the blood.
The kidneys have many functions, including:
- Removal of wastes and excess fluids by cleaning and filtering the blood, and producing urine.
- Production of hormones which help maintain healthy bones, control blood pressure and control the production of red blood cells which carry oxygen around the body.
What is kidney failure?
Kidney failure may be described as a loss in the kidney’s ability to filter (remove) waste products from your blood. Kidney failure can happen quickly, caused by for example a sudden loss of large amounts of blood, or an accident and this is called acute kidney injury. Acute Kidney Injury is usually short lived, but can occasionally lead to lasting kidney damage. It may also be abbreviated to AKI.
More commonly, kidney function worsens over a number of years and this is called chronic kidney failure or Chronic kidney disease (often abbreviated as CKD). The National Kidney Foundation state that up to two thirds of CKD is caused by uncontrolled diabetes or high blood pressure (hypertension). CKD is usually not reversible but if found early, progression can be delayed through medication, diet and lifestyle changes by maintaining current kidney function.
What is the definition of chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as the presence of kidney damage, or a decreased level of kidney function, for a period of three months or more.
Signs of kidney damage include:
- Persistent small and large proteins in the urine (proteinuria and microalbuminuria)
- Persistent blood in the urine (haematuria) – after exclusion of other causes, e.g. urological disease.
- Structural abnormalities of the kidneys demonstrated on ultrasound scanning or other radiological tests e.g. polycystic kidney disease, reflux nephropathy
- Biopsy proven chronic glomerulonephritis
The Irish Nephrology Society currently recommends classifying Chronic Kidney Disease into five stages based on a measure estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
Sometimes CKD can lead to end stage kidney disease, (ESKD) which requires dialysis or a transplant to keep you alive. However, as the Irish Nephrology Society (INS) state, ‘the vast majority of patients with mild to moderate CKD will not require dialysis and can be managed in primary care’. Early detection and treatment may help prevent ESKD and the need for dialysis or transplant treatment. The kidney diet is one of the cornerstones of the treatment of CKD and helps with the target of delaying progression. The kidney diet is also essential in maintaining quality of life and functional capacity in people with kidney disease. The type of kidney diet required is individualised to the stage of kidney disease (based on eGFR), other diseases present (co-morbidities), the person’s age, weight and social situation. Some examples of important kidney diet changes in the early stages of CKD are ‘A No Added Salt’, ‘Weight Reduction’ (if overweight) and ‘Moderate Protein Intake’. A Kidney (Renal) Dietitian can assess your diet needs and advise on a tailor made kidney (renal) diet.
How do I know if I have CKD?
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is sometimes called a silent disease because there are often no warning signs. Some signs of CKD are:
- Weight loss and poor appetite
- Swollen ankles, feet or hands (due to water retention)
- Shortness of breath
- Blood or protein in your urine
- An increased need to pass urine, particularly at night
- Itchy skin
- Muscle Cramps
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Nausea
- Erectile Dysfunction in men.
You often will not know if you have CKD as you may not experience any symptoms, however screening is based on simple urine and blood test that your doctor can easily perform. If you have high blood pressure or diabetes or you are obese, yearly screening should be considered with your doctor.
Remember! Early detection of CKD may allow you to delay progression through diet and lifestyle changes and medication.
Do I require daily Vitamin supplementation if I have Chronic Kidney Disease?
‘Can the kidney diet provide your complete nutritional needs or do you require daily vitamin supplementation? Here, the Kidney (Renal) Dietitians discuss vitamins and chronic kidney disease’
Vitamins are substances needed by your body to help carry out special functions. Vitamins are divided into two categories;
Water soluble vitamins i.e. Vitamins B, C and Folate
Fat soluble vitamins i.e. Vitamins A, D, E, K
Vitamins play a part in controlling the body’s ability to burn fat and sugar for energy, and build proteins for growth. If vitamins are deficient, these reactions are not properly coordinated, and may cause, muscle weakness, fatigue and nerve pain. Following a balanced diet is the preferred way to get the recommended amount of these vitamins, however patients with kidney disease often cannot get enough of some vitamins,
Reasons include:
- The degree of dietary restriction required in your kidney diet which can limit your intake of water soluble vitamins
- Presence of a poor appetite or malnutrition.
- Disruption in meal times due to treatments and appointments.
- The waste products that build up in your body each day can change the way your body uses vitamins.
- Medications which may interfere with the absorption or activity of certain vitamins.
- The Dialysis process which can result in loss of certain vitamins.
- Chronic Kidney disease reduces production (e.g. Active Vitamin D)
Due to the above, patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) may require a daily vitamin supplement as well as a balanced, nutrient dense kidney diet.
Special renal vitamins are usually prescribed to patients to provide the extra water soluble vitamins needed. Discuss your requirement for vitamin supplementation with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Folic Acid (Folate) and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dietary Folic Acid (Folate) intake may be suboptimal due to;
- reduced food intake,
- education regarding a low potassium and low phosphate diet which can result in restriction of fruit and vegetables (which are high sources of dietary folic acid (folate),
- altered metabolism of folic acid (folate),
- impaired production,
- and dialysate losses of water soluble vitamins.
Discuss your requirement for folic acid (folate) supplementation with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Vitamin D and Chronic Kidney Disease
Vitamin D helps your body to absorb calcium and phosphate and regulates the production of parathyroid hormone (a hormone that controls bone turnover). In CKD the kidney loses the ability to make active vitamin D. Supplementation with a special active vitamin D may be necessary. This is determined by blood levels of calcium, phosphate and parathyroid hormone (PTH). Supplementation with native Vitamin D (inactive form) may also be required. Discuss the need for vitamin supplementation with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Can vitamin Supplementation cause harm?
Yes, when the kidneys are not able to eliminate excess vitamins from your body they can build up to toxic levels, this is of particular concern for Vitamin A (fat soluble vitamin), which is contained in many over the counter multi-vitamin preparations.
Also, Vitamin C breaks down in the body into a crystal called oxalate. Healthy kidneys remove extra oxalate, but dialysis is much less effective. A build up of oxalate can cause bone and joint deposits and pain.
Only use the vitamin supplement approved by your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Do not take an over the counter multi-vitamin supplement.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following tips may be useful to help manage your thirst on a fluid restriction:
- Don’t eat salty and very spicy foods as they will make you thirsty and make it difficult to limit your fluids. Ask your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian for an individualised list of salty foods to avoid and other flavourings for your food.
- Use a small cup or glass. Measure the volume and work out how many you can drink in a day.
- If your mouth is very dry, rinse regularly. Check with your doctor if any of your medications have thirst or dry mouth as a side effect.
- If you have diabetes and your blood sugars are high, this will make you very thirsty. Talk to your Doctor or Dietitian to see what you can do to improve your levels.
- Sucking on an ice cube can be refreshing and last longer than a sip of water. For a change try freezing some diluted cordial in your ice cube tray. Remember to take this from your fluid allowance. 1 ice-cube = 15mls of fluid and use No Added Sugar varieties if you have Diabetes.
- If your mouth feels fresh , it won’t feel as dry. Brush your teeth or use a mouthwash regularly or chew gum. Lip salve (balm) can also be used for dry lips.
- Measure your daily milk allowance as part of your overall fluid intake.
- A portion of fruit within your fruit allowance can be used to refresh your mouth.
- Extra strong mints can help manage thirst.
- There are pharmaceutical gels and sprays available from your local chemist which can help manage your dry mouth. Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian or Doctor can advise you regarding specific products.
There are a variety of herbs and spices that can be used as a substitute for salt from garlic and pepper to basil, oregano and rosemary. You can flavour your meals in many different ways. Remember to use herbs and spices sparingly.
Some suggested flavour combinations:
Food Suggested flavouring
Beef: Allspice, dry mustard rubbed into the meat before cooking, oregano, bay leaf, chilli powder, cayenne pepper
Fish: Vinegar, lemon, dill, mint, thyme, garlic, chilli
Pork: Cloves, apple, garlic, onion, sage, curry powder
Chicken: Lemon, garlic, tarragon, rosemary, sage, thyme, chilli powder, cayenne pepper, paprika
Stews & casseroles: Bouquet garni, oregano, sage, thyme, basil, garlic
Recipes
Low salt gravy
Ingredients:
- Meat juices
- Gravy browning (to add colour and flavour)
- Cornflour
- Flavourings such as herbs, spices, onions
Method:
- Allow the meat juices to cool and skim off the fat.
- Thicken with cornflour.
- Add gravy browning until the desired colour is reached.
- Don’t use stock cubes or gravy mixes.
Marinade
Ingredients:
- 3 tablespoons/ 50ml oil (olive oil or rapeseed oil)
- 2 tablespoons/ 30ml wine vinegar
- 1 clove of garlic – chopped
- Black pepper
- Parsley and thyme/ alternative herbs or spices as desired
Method:
- Place all ingredients in a non metallic bowl
- Place the meat/ fish/ poultry pieces in the bowl and cover with the marinade and stir well.
- Cover the bowl and place in the fridge
- Marinade for 15 min to 2 hours depending on how strong you want the marinade flavour to be.
Soaking potatoes may remove some potassium but it will not remove as much as double boiling.
There are two cooking methods you can use to significantly reduce the potassium content in your potatoes. The first method is often referred to as “double boiling”. The second method involves cutting the potatoes into smaller pieces and cooking in a much larger volume of water.
Method 1:
Peel the potatoes and cut into thin slices. Bring to the boil, using four times as much water as potatoes. Throw the water away, and replace with the same volume of fresh boiling water. When cooked, drain and measure your allowance.
Method 2:
Peel and dice potatoes into 1cm cubes. Bring to the boil in 10 times as much water as potatoes. Cook until potatoes are soft. When cooked, drain and measure your allowance.
These methods will reduce the potassium content by at least half the original amount.
If boiling isn’t the planned cooking method, potassium may still be reduced by slicing or cutting potatoes into small pieces or grating them and soaking them in a large amount of water at room temperature or warmer for greater potassium removal.
The least effective method of removing potassium is to soak potatoes in the fridge, then prepare without boiling first.
It is still very important to watch your portion size of potatoes, as even “double boiled” potatoes still contain a considerable amount of potassium.
Going for a meal out should be an enjoyable experience and one that you can continue to look forward to despite the need to maintain your renal diet. Here are some tips to help you achieve this challenge.
Plan Ahead
If you know you will be eating out, cut back on serving sizes early in the day and avoid any salty or high potassium foods. If you are on a fluid restriction you may wish to save your fluids throughout the day to allow more when you are eating out. If you are on phosphate binders remember to bring them with you and take them with your meal. Talk to your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian about eating out and which local restaurants are best for you.
Read the menu carefully
Ask questions about any menu items you are not sure of. If you’re not comfortable asking in front of your dinner companions – call ahead or check out the menu online!
Special Requests
Many restaurants will be only too happy to make substitutions (i.e. rice instead of potatoes) or serve salad dressings, sauces and gravies on the side so you can control the amount you eat. Ask if your meal can be cooked without extra or added salt.
Keep in mind that anything you eat in a restaurant will be saltier than what you have at home – remember moderation is the key.
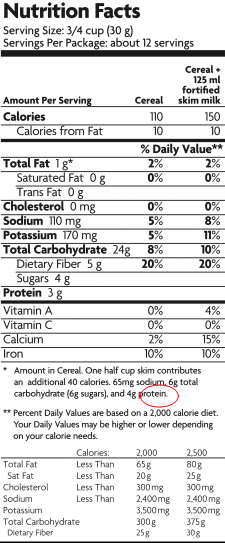
Product labels on many foods show how much sodium (mg/g) or salt (mg/g) they contain. Sodium is not the same as salt. Salt is sodium chloride so sodium is just one part of a molecule of salt. Many labels provide sodium content but not the salt content which can be confusing. If the salt content is not available on a label you can calculate it from the sodium content using the following:
Sodium x 2.5 = salt content or Salt ÷ 2.5 = sodium content
If you have kidney disease a good goal for sodium intake is 2300 mg of sodium or 6g salt per day. Check with your Doctor or Kidney (Renal) Dietitian to confirm what your maximum daily salt (sodium) limit should be.
Nutrition information may be presented in two ways.
Per serving – shows the amount of each nutrient that is contained in a specified serving size. If using this information, check if your portion is larger or smaller, for example a bowl of cereal may be presented as 30g on the nutritional information but your bowl may contain 50g. You would therefore calculate your portion’s nutritional content as follows:
Calories : (110 /30 ) x 50 = 183 calories
Per 100g – shows the amount of each nutrient that is contained in 100g of the food. If a portion contains more than 500mg/0.5g of sodium or 1.25g of salt it is a high salt option.
‘Double boiling’ a peeled and chopped potato removes up to 50% of the potassium in the potato.
‘Double boiling’ is the term used to describe, one method of producing low potassium potatoes.
The potatoes are peeled, chopped into small pieces and placed into a large pot of boiling water (ratio 4:1 water: potato). The water is brought to the boil, discarded & replaced with a large amount of fresh boiling water (ratio 4:1 water: potato). The potatoes are cooked in this water and the water is then drained before measuring the potato allowance.
An average peeled and boiled potato (175g) contains 490mg / 12.5mmol potassium and double boiled this will reduce to 245mg / 6.3mmol potassium.
Click here to learn more about preparing low potassium potatoes.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) usually develops gradually over time…
so if you find out you have kidney disease; you have an opportunity to slow down the loss of kidney function by making some changes to your diet and lifestyle.
If you have high blood pressure…
controlling your blood pressure is a very important way to help slow down the decline in kidney function. Dietary measures to help control blood pressure include reducing salt intake, drinking less alcohol and losing weight if overweight. Lifestyle measures such as stopping smoking and taking regular exercise will also help control blood pressure.
If you have diabetes…
controlling your blood sugar (glucose) levels and maintaining a healthy weight, or losing weight if overweight will help slow the development of kidney disease.
If you have raised cholesterol levels…
dietary measures including reducing your total fat intake; and your intake of saturated fat (including butter, fat on meat/ skin on poultry), can help lower cholesterol and thereby reduce your risk of heart problems.
In early CKD…
keeping your portions of protein rich foods (such as meat, fish, eggs, dairy products and pulses) to modest amounts may help to slow down the decline of kidney function. It is important to include protein foods in your diet, however large portions are not recommended. Your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian can give you more individual advice.
Herbal supplements can be unsafe for people with kidney problems. Stop taking your herbal supplement until you check its safety with your Doctor or Dietitian.
A Dietitian is a health professional who is qualified to give accurate advice and information on all aspects of nutrition and diet.
The Dietitian will help to match your nutritional needs to your medical conditions. Ask your General Practitioner or Consultant to refer you to a Dietitian or click here to access a private Dietitian.
When following a renal diet you will be asked to limit your salt intake…
Salt is mostly made up of the minerals sodium and chloride. You may see sodium or sodium chloride written on food labels instead of salt.
Limiting your sodium intake…
helps keep blood pressure under control and minimizes swelling in the body (oedema).
Sea salt is made from evaporated sea water…
with little processing and contains trace amounts of minerals that may give it a different flavour or colour than table salt whereas table salt is mined.
However, sea salt and table salt contain about the same amount of sodium…
Try to avoid adding any salt to your food.
Even without adding salt to your food, you can easily get more than you need by eating foods that have a high salt content. Try to choose fresh foods instead of processed and canned food.
Carob is similar to chocolate. They are both high in potassium and phosphate.
Unfortunately, it is not a good substitute for chocolate. Speak with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian regarding your current blood results to find out how much chocolate, if any, can be incorporated into your diet.
No matter what stage of Chronic Kidney Disease…
diet plays an essential role in treating kidney disease. In early Chronic Kidney Disease, restricting protein intake to a moderate level may help delay the progression of disease. This restriction should be planned carefully with your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian to avoid nutrient deficiencies occurring.
High blood pressure…
is one of the leading causes of Chronic Kidney Disease, and salt has been shown to play a role in contributing to high blood pressure. A lot of the salt we take is hidden in processed or packaged foods. You could start by cutting back on processed foods (such as packet soups and sauces, processed meat and meat products) and choosing more fresh foods. Using herbs and spices instead of salt in cooking and at the table will help flavour your food. See the section on food labels for more information on what to look out for when reading food labels.
Diet helps control high potassium and phosphate levels…
which can develop in kidney disease. At all stages of Chronic Kidney Disease, restricting salt intake is very important for controlling blood pressure and helping to reduce fluid overload.
For individualised dietary advice, talk to your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian or ask your Doctor to refer you to one.
No. Protein is an essential nutrient for everybody as part of a well-balanced diet.
However… the amount you need each day will depend on the stage of your kidney disease.
As your kidney disease progresses… you may be told to reduce your protein intake. This is because your kidneys may not be able to able to excrete the waste products if you eat too much.
With end stage kidney disease… if you are on dialysis you will need to eat more protein each day as protein is lost from your body during the dialysis procedure.
The exact amount of protein required… is individual for everybody and is based on your body weight. Talk to your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian about how much protein you need and which food sources are best for you.
‘Advice from the Kidney (Renal) Dietitians on the importance of avoiding food containing phosphate additives’
Phosphate additives are added to foods for many reasons. They can be used to extend shelf life, improve colour, enhance flavour, or retain moisture.
The phosphates in food additives are especially dangerous if you have kidney disease since our bodies absorb them much more efficiently than the phosphates that occur naturally in foods like dairy foods, lentils and whole-grains.
Unfortunately there is no complete list of all foods containing phosphate additives because there are too many of them. Some examples of processed foods which may contain these additives are listed below.
Processed meats, processed fish and cheese, dried foods, dessert and cake mixes, cola drinks, alcoholic beverages, salt substitutes, instant pasta, sauces and bakery products.
Many products marketed as “low sodium” contain high amounts of phosphate additives. Cold meats with phosphate additives may contain up to 70% more phosphates than brands containing no additives.
How to avoid phosphate additives in your Kidney Diet = Read the Labels
Reading labels is the key. Try to read the food labels of processed foods that you use regularly. Food additives are considered ingredients and must be listed in the ingredients list by specific name or designated E number.
The most common ones are listed below:
E338 Phosphoric acid
E339 Sodium phosphates
E340 Potassium phosphates
E341 Calcium phosphates
E343 Magnesium phosphates
E450 Diphosphates
E540 Dicalcium diphosphate
E541 Sodium aluminium phosphate
E542 Bone phosphate
E544 Calcium polyphosphates
E545 Ammonium polyphosphates
Foods containing these ingredients are best avoided on the Kidney (Renal) Diet.
Compare products and choose those without phosphate additives.
Look for foods labelled “free from artificial colours, flavours and preservatives”.
If you need help or advice ask your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Potassium…
is a mineral that is in many of the foods we commonly eat. It is true to say that some foods contain higher amounts of potassium than others.
You may need…
to restrict the amount of potassium in your diet if you have a high potassium blood level and depending on the stage of your kidney disease.
In general all fruit, vegetables and potatoes…
are high in potassium and within this, some have higher amounts when compared to others.
As a general rule…
the high potassium fruits are bananas, all dried fruits and fruit juices. Some other foods known to be high in potassium include coffee, chocolate, salt substitutes, beer wine, nuts and crisps.
The portions of these foods you eat are important…
you will need to talk to your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian about this as every individual is different.
The cooking method used for high potassium foods…
like vegetables and potatoes can also be important. Boiling all vegetables and potatoes and possibly ‘double boiling’ potatoes may be needed depending on your stage of kidney disease. Here’s a low potassium potato cooking method.
Phosphate…
is a mineral found in most foods we commonly eat. The foods considered to have the highest amounts of Phosphate are protein rich foods such as dairy based products (e.g. milk/cheese/yoghurts) and all types of meat, fish and poultry.
It is important…
to note that protein rich foods should not be excluded from your diet as protein has many important functions. To clarify whether you need to restrict your phosphate intakes and how to do it without compromising your protein intake you should contact your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian for guidance.
Other high phosphate foods…
include nuts, seeds, wholegrain foods and foods containing bran. Phosphate food additives also contribute significantly to the amounts of Phosphate in our diets.
To help avoid these additives…
it would be important to read food labels and identify the foods where Phosphate has been added. ‘Phosphate’ can be labelled in a number of ways such as; phosphorous, phosphates, hexametaphosphates, diphosphates, triphosphates, polyphosphates etc.
The answer to this question can vary depending on if you want to maintain healthy kidneys or if you have been diagnosed with kidney disease and would like diet information based on your diagnosis.
For overall general health, it is recommended to follow a well-balanced diet which includes all food groups.
The Department of Health’s Food Pyramid is a useful guide. It is important to watch your salt intake as many of us consume more than the recommended amount of salt on a daily basis.
High blood pressure is a leading cause of kidney disease and salt intake plays a role in high blood pressure. Even without adding salt to your food, you can easily get more than you need by eating foods that have a high salt content.
Try to choose fresh foods instead of processed and canned food. Start reading food labels to identify how much salt is in the foods you choose. Another name for salt is sodium or sodium chloride and you may see this written on food labels.
A Dietitian is a food and nutrition expert….
During the stages of kidney disease you may need to alter the foods you eat.
This is because patients with kidney disease must take care when it comes to the foods they choose…
as some may be harmful to their health.
The Kidney (Renal) Dietitian can advise and explain the best food choices for your stage of kidney disease…
and help you maintain good nutritional health. Each individual with kidney disease will have specific dietary needs and your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will guide you on the best food choices for you
Your fluid restriction should include all sources of fluid
e.g. tea, squash, milk, water, dietary supplements and water taken with medications.
Be aware of foods with a high fluid content,,,
for example jelly/ custard/ ice-cream/ yogurt count as ½ fluid e.g. 200mls milk pudding = 100mls fluid. Try to choose alternative desserts.
A Dietitian is a health professional who is qualified to give accurate advice and information on all aspects of nutrition and diet. A Kidney (Renal) Dietitian provides specialist advice to people with chronic kidney disease and works as part of a renal multi-disciplinary team to help manage complications of kidney disease and improve quality of life.
Role of Kidney (Renal) Dietitian
Nutrition and diet play an integral role in the management of kidney disease. However, there is no one diet that is right for everyone with kidney disease. Your dietary requirements will change over time depending on how much kidney function you have.
The Kidney (Renal) Dietitian will assess when you need to make dietary changes based on your most recent blood results and nutritional status. After your initial consultation with the Kidney (Renal) Dietitian you will be given your own individualised diet which will be reviewed and changed as necessary.
You should treat a low blood glucose (sugar) level immediately
with rapid-acting carbohydrates such as:
- 150mls ordinary 7up or orange (small glass)
- 5 dextrose/ Lucozade tablets
It is therefore important to carry a hypo treatment
with you at all times. After 10-15 minutes check your blood glucose (sugar) levels again:
If less than 4mmol/L
take another rapid acting carbohydrate source as above.
If greater than 4 mmol/L
and you are due a meal or snack within the next hour, you will not need to take any additional carbohydrate until then. However, if not eating for over an hour you should take additional carbohydrate to maintain your blood glucose (sugar) such as:
- A slice of bread
- A digestive / 2 Rich tea biscuits
- A portion of fruit
Foods which are NOT suitable for immediate treatment of low blood glucose (sugar) include: chocolate, crisps, biscuits, sandwich, cup of tea with milk and sugar. This is because it takes too long for the glucose (sugar) to be released from these foods. Orange juice is not suitable as it is high in potassium.
Important Notice:
The nutritional content of Lucozade Energy is changing
The carbohydrate content of Lucozade Energy is being reduced by approximately 50%. Therefore you will need to take more Lucozade to correct your hypoglycaemic (low blood sugar) episode.
From April 2017, the new Lucozade bottles and cans will be available. For a period of time, both old and new versions may be on the shelves together. It is therefore important that you remember to check the label for the amount of carbohydrate it contains.
To correct a hypo (low blood sugar level) you need to take 15g of rapidly absorbed carbohydrate. The new Lucozade product contains 8.9g carbohydrate per 100mls. Therefore you will now need to take 170mls to get 15g of carbohydrate to correct your hypo.
It is important to check labels regularly to ensure you are getting the right amount of carbohydrate as other brands of fizzy drinks may also change their sugar content
Barbara Gillman, Clinical Specialist Renal Dietitian, Mater Misercordiae University Hospital
Those on dialysis…
are at increased risk of reduced vitamin levels due to losses during dialysis and dietary restrictions. A daily water soluble vitamin supplement which is suitable for renal patients may be recommended by your Kidney (Renal) Dietitian. It is advisable to discuss any vitamin / mineral supplements you are taking with your doctor / Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Kidney disease patients should avoid taking any multivitamin…
without first speaking with your Doctor or Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
Some people with kidney disease need to take renal specific vitamin supplements…
including a form of Vitamin D, water soluble vitamins and folic acid.
This should only be done…
under the supervision of your Doctor or Kidney (Renal) Dietitian.
White bread is lower in potassium and phosphate than whole meal bread…
and therefore is recommended for those with reduced kidney function, particularly if your blood levels of potassium and phosphate are high.
As kidney function declines…
so does the kidney’s ability to filter potassium and phosphate.
To limit potassium and phosphate…
choose lower potassium and phosphate products like white bread (sliced or rolls), granary bread, ciabatta or white pitta bread.
We are delighted to see this website coming from the Renal Interest Group – we regularly get calls from patients, and their families, seeking information on the renal diet and this will be a great resource.
- Maire Leddy SheridanClinical Nurse Manager, Renal Dialysis Unit Cavan and Monaghan Hospital Group
I feel this informative website will empower patients to look at their own diet and strive to improve their quality of life. I wish to thank all involved in getting this of the ground.
- Val TwomeyAuthor of Truly Tasty
I would like to congratulate the renal dietitians from the Renal Interest Group of the Irish Nutrition and Dietetic Institute for such a wonderful, informative, eye catching patient education site. Just Brilliant!
-

The Kidneys:
An Introduction
-

Diet & Lifestyle
-

Stages of
Kidney Disease